By Philips 188
BT134 is a bidirectional silicon controlled rectifier (SCR) device, also known as a bidirectional controllable rectifier transistor. SCR is a semiconductor device commonly used to control the flow of electricity. BT134 is one of the models with specific electrical characteristics and applications.
Controlled BT134 is a three-terminal bidirectional thyristor with high sensitivity, high reliability and high stability. It is a semiconductor device mainly used to control the on and off of alternating current and adjust the voltage.
Ⅰ.Specification parameters of BT134
•Mounting type:Through hole
•Operating temperature:125℃
•Surface mount:NO
•Packaging:Tube
•JESD-30 code:R-PSIP-T3
•Voltage-off state:600V
•Terminal surface treatment:Sn
•Current - non-repetitive surge 50, 60Hz (Itsm):25A\27A
•Triac Type:Logic-Sensitive Gate
•Voltage-gate trigger (Vgt) (max):1.5V
•Current - Gate Trigger (Igt) (max):5mA
•Current-on-state (It (RMS)) (maximum):4A
Ⅱ.Working principle of BT134
1.Four-layer structure: BT134 is a transistor with a four-layer semiconductor structure. Its structure is NPNP. This structure is usually called a tetrode, or in some cases, a double diode. It has two PN junctions, one between its two outer layers. A four-layer semiconductor structure usually consists of two pairs of P-type and N-type semiconductor materials, each pair separated by |-type (intrinsic) semiconductor material. This structure has two PN junctions, one at the top and another at the bottom. Each PN junction can be thought of as an individual diode, but when they are connected by a semiconductor material, they interact as a whole. This type of transistor is commonly used in high-frequency, high-voltage applications such as switching power supplies and amplifiers. Its advantages include high switching speed, low conduction losses, and good thermal stability.
2.Bidirectional conduction: Unlike one-way thyristor, BT134 is a two-way thyristor, which means that once triggered, current can flow in both directions, positive half cycle and negative half cycle. This makes the BT134 suitable for AC circuits, capable of controlling a portion of the entire AC waveform. This bidirectional conductivity makes the triac more suitable for use in AC circuits because it is able to control the entire waveform of the AC current, not just half a cycle. In an AC circuit, the direction of the current changes between positive and negative half cycles, so a triac is able to effectively control the current in both directions. This property makes triacs very useful in many applications such as AC power switching, motor control, etc. Unidirectional thyristors are mainly used in DC circuits, but they can only control current in one direction.
3.Trigger: The work of BT134 starts from triggering its trigger end. When the voltage applied to the trigger terminal exceeds a specific trigger voltage (also called gate voltage or trigger voltage), the device will begin to conduct. This process involves the generation of an electron-hole pair in the PNP junction, initiating conduction.
4.Sustain: Once the BT134 is triggered and turned on, it will remain on until the current drops to zero or close to zero. This is because once activated, the electron and hole pairs within the PNP junction will continue to maintain a conductive state.
5.Turn off: To turn off BT134, it can be achieved by reducing the current or applying reverse voltage. When the current drops to zero, the BT134 will automatically shut down.
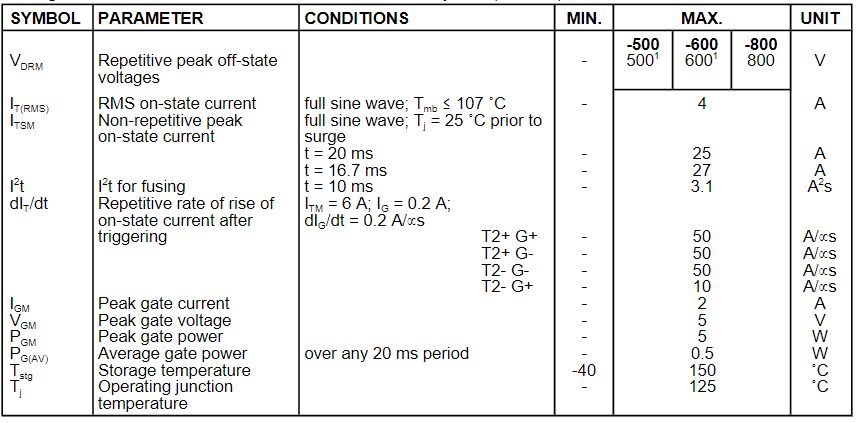
Ⅲ.Limiting Values of BT134
Limiting values in accordance with the Absolute Maximum System (IEC 134).
Ⅳ.Protective characteristics of BT134
1.Overcurrent protection: BT134 is usually designed to withstand current within a specific range. If the current exceeds the set maximum value, the device may limit the current through its own protection mechanism to prevent overcurrent from causing damage to the device.
2.Temperature protection: Excessive temperature may cause damage to semiconductor devices. Therefore, BT134 is usually designed to operate normally within a certain operating temperature range and has an overheating protection mechanism to prevent the device from being damaged beyond its withstand temperature.
3.Overvoltage protection: BT134 also has certain resistance to overvoltage. Overvoltage may occur in unexpected situations in the circuit, but the BT134 should be able to operate within a reasonable voltage range while avoiding device damage.
4.Overvoltage shutdown: In some cases, if the voltage exceeds the rating of BT134, the device may automatically shut down to protect itself. This helps prevent excessive voltage from causing irreversible damage to the device.
5.Current Limiting: The BT134 may contain some current limiting features to avoid current exceeding safe levels under abnormal conditions. This helps maintain device stability and long life.
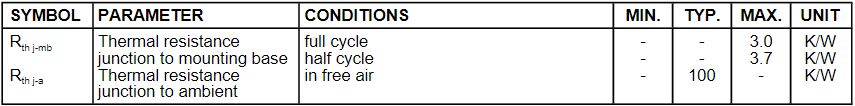
Ⅴ.Thermal Resistances of BT134
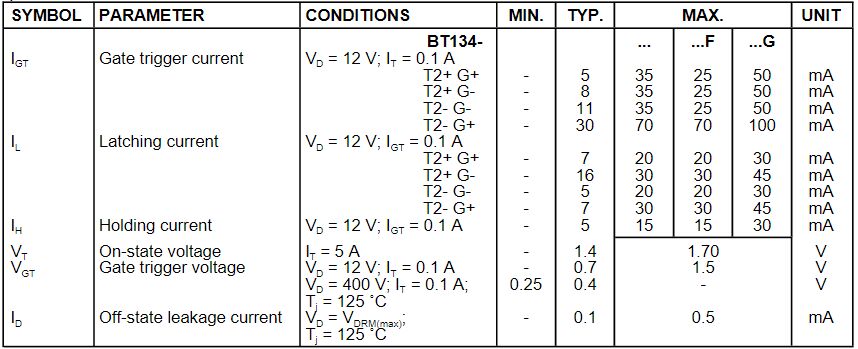
Ⅵ.Static Characteristics of BT134
Tj=25℃(less otherwise stated)
Ⅶ.Application fields of BT134
1.Lighting control: BT134 is a silicon controlled thyristor (Triac), which is often used in dimming circuits. It allows the brightness of the light to be adjusted by giving it appropriate control. This kind of control is very common in home lighting, office lighting and other occasions. The basic principle of the dimming circuit is to adjust the brightness of the light by controlling the on and off of the current. When the current is on, the light is bright, and when the current is off, the light is dark. As a thyristor, BT134 is used to control the on-off current in the circuit. By changing the firing angle of BT134, the waveform of the current can be controlled, thereby adjusting the brightness of the light.
2.Electronic equipment power switch: BT134 can be used as a power switch in electronic equipment, allowing the power status of the equipment to be controlled by controlling the current.
3.Electric furnace and heating control: Since BT134 is able to control current, it can be used for the control of electric furnaces and other heating devices, allowing it to adjust the heating level as needed.
4.Temperature controller: In some temperature control systems, BT134 can be used to control the heating element to maintain a set temperature level.
5.Motor control: BT134 can be used as a switch for the motor in the control circuit of a small motor to realize the start, stop and speed regulation of the motor. In the control circuit of the motor, the function of BT134 is mainly to control the on-off and adjustment of the current. The size of the current is used to control the motor. When BT134 is on, current passes through the motor, causing the motor to run; when BT134 is off, the current is disconnected and the motor stops running. For motor speed regulation, it can be achieved by changing the firing angle of BT134. By changing the firing angle, the waveform of the current can be changed, thereby changing the speed of the motor. In addition, the start, stop and speed regulation of the motor can also be realized by controlling the on and off time of BT134.
6.Electric vehicle charging control: In electric vehicle charging piles, BT134 can be used to control the charging current to adapt to different types of electric vehicles and charging needs.
7.Power tools: In some power tools, BT134 can be used to control the speed and power of the motor, thereby providing more flexible working conditions.
Ⅷ. Advantages of BT134
1.Simple triggering and control: BT134 can be triggered by applying a specific trigger voltage. Once triggered, the device remains on until the current drops to zero or close to zero. This simple triggering and control makes the BT134 easy to integrate into a variety of circuits.
2.Bidirectional conduction: BT134 is a two-way thyristor that can control current in both directions of the positive half cycle and the negative half cycle. This makes it ideal for AC circuits, capable of controlling a portion of the entire AC waveform.
3.Suitable for high-power applications: BT134 can handle relatively high currents and voltages, making it suitable for some high-power applications, such as electric furnace control, motor control, etc.
4.High reliability: SCR devices usually have high reliability and long life. They can operate over a wide temperature range and are relatively insensitive to changes in environmental conditions.
5.Wide range of applications: Due to its bidirectional conduction characteristics, BT134 can play a role in various applications, including lighting control, heating control, power tools, electric vehicle charging control and other fields.
6.Cost-Effectiveness: SCR devices typically have relatively low manufacturing costs, which helps make the BT134 an affordable choice in many applications.
Frequently Asked Questions
1.How to trigger and control BT134?
Trigger voltage: The trigger of BT134 is achieved by applying a trigger voltage to the trigger terminal (Gate) of the device. When the trigger voltage exceeds a specific gate voltage (also called the trigger voltage), the BT134 will enter the conductive state. Trigger current: In addition to the trigger voltage, sufficient trigger current needs to be provided to ensure that the BT134 can trigger reliably. Trigger current refers to the current flowing through the trigger terminal under the trigger voltage. Trigger mode: BT134 can achieve conduction through different trigger modes. The most common way is to use pulse signals or periodic trigger signals. The purpose of these signals is to trigger the BT134 at specific times of each AC cycle, causing it to conduct for a certain period of time.
2.Is BT134 available in DC circuit?
BT134 is designed for AC circuits. Its conduction characteristics are bidirectional and can control the current in both directions of the positive half cycle and the negative half cycle. In a DC circuit, since current flows in only one direction, the bidirectional conduction characteristic of the BT134 would become redundant and could lead to unnecessary complexity in practical applications. In DC circuits, triggering and switching off the BT134 may not be as simple as in AC circuits. Due to the cyclical changes in AC circuits, triggering and shutdown can more easily correspond to the zero-crossing point of the current. In DC circuits, this timing may require additional control circuitry to ensure accurate triggering and shutdown.
3.What distinguishes BT134 from other bidirectional thyristors?
BT134 is a specific model of bidirectional thyristor. The differences between BT134 and other similar devices lie in their electrical characteristics, triggering requirements, and application-specific features.